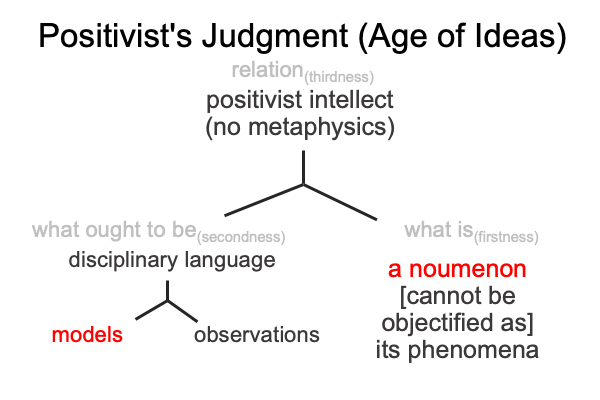
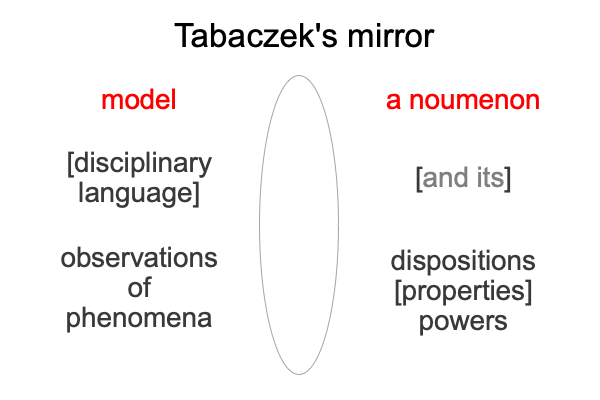
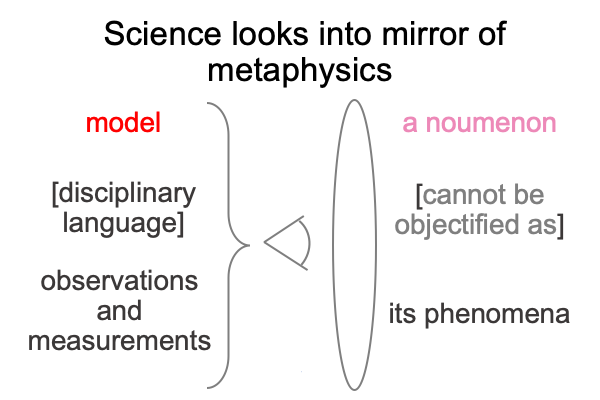
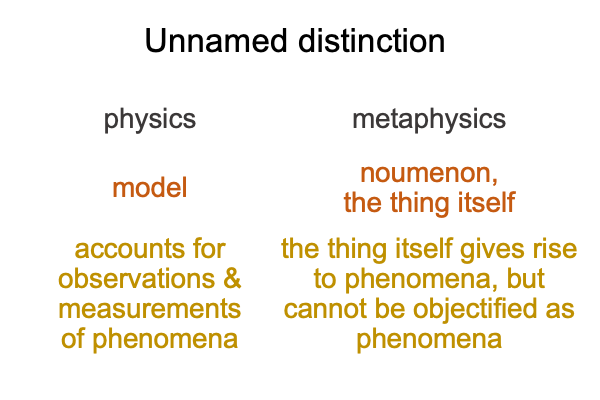
A First Look at Julian Jaynes’s Book (1976) “The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind” (Part 1 of 21)
0236 Why do I examine this work?
I reviewed Steven Mithen’s book, The Language Puzzle: Piecing Together The Six-Million-Year Story Of How Words Evolved (2024, Basic Books, New York). See Razie Mah’s blog for September 2025. The examination concludes on point 0235.
During the examination, I recall a book that Julian Jaynes publishes in 1976.
I wonder, “Why does Mithen’s book remind me of Jaynes?”
I now have a copy of The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind (First Mariner edition (2000), New York, New York) before me.
This explains why I start the current examination on point 0236.
0237 Julian Jaynes (1920-1997 AD) earned master and doctoral degrees in psychology at Yale University. He lectured in psychology at Princeton from 1966 to 1990. In 1990, he writes a postscript that appears in the Mariner edition.
This afterward lists the four hypotheses in Books I and II. Plus, the postscript expands on Part III, by discussing the psychological transition from the bicameral mind to subjective consciousness at the end of the Bronze Age in the Near East.
0238 Here is the list.

0239 So, why does Mithen’s book remind me of Jaynes’s work?
My review of The Language Puzzle led me to conclude that Mithen’s explicit rejection of a gestural origin of languageprevents him from realizing that his information implicitly supports the very position that um… he rejects.
Yes, if I ignore his declaration against a gestural origin to language, then I can start to recognize that speech is added to fully linguistic hand-talk after the domestication of fire, when the community becomes a social circle under pressure from natural selection.
0240 That reminds me of a curious pun that seems to have import in the year 2025AD.
The Russian word for “no” is “nyet”.
To the American ear, “nyet” sounds like “not yet”. And, that means, “Yes, but not now.”
So, when Mithen says, “nyet”, to the gestural origins of language, his English speaking bicameral mind hears, “not yet”. So, Mithen unwittingly drops clues to his nyet hypothesis within his own subjectively conscious argument. These hints offer a weird twist to Looking at Steven Mithen’s Book (2024) The Language Puzzle. It is as if Mithen’s own bicameral mind offers – what I will call – “a nyet hypothesis”.
0241 Now, consider the first two hypothesis (A and B) in Jaynes’s Books I and II.
First (A), subjective consciousness relies on spoken language. Mithen consciously proposes that spoken words are built over millions of years through synaesthesia, cross modal “leakage” of sensations, from visual things and events to auditory vocalizations.
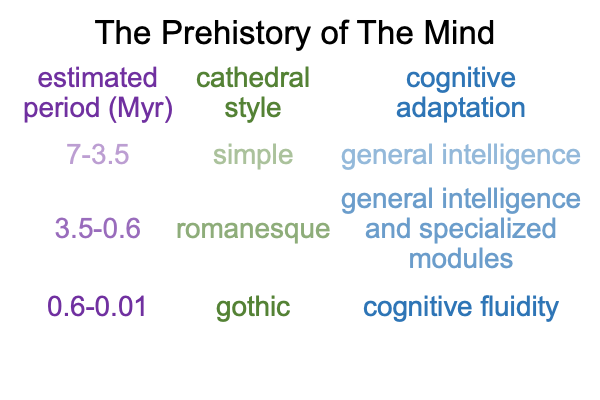
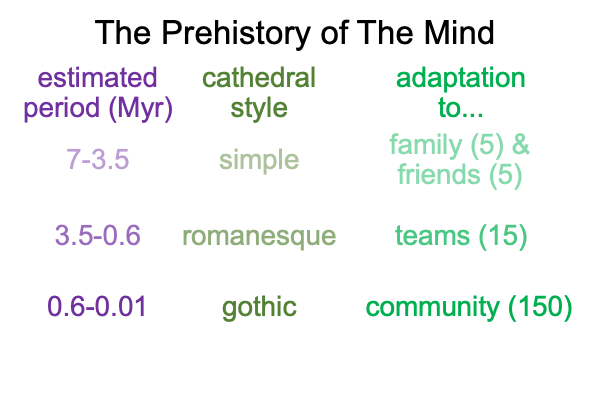
0242 Of course, this proposal comes across as sketchy. Why would early hominins, such as the australopithecines and the early species in the Homo genus (3.5 to 0.6Myr – millions of years ago) do this? And how? The voice is most likely not under voluntary control. Involuntary calls rule the day.
But, the vocal tract changes over time. Most likely, the voice is on the verge of coming under voluntary control by the time that Homo heidelbergensis appears in the fossil record (perhaps, over 600kyr – thousands of years ago).
On top of that, Homo heidelbergensis shows up during the period when hominins domesticate fire (800-400kyr). So, Mithen consciously and cautiously suggests that the synaesthesia business really takes off around that time.
0243 The nyet hypothesis?
Well, of course, proto-linguistic hand talk has plenty of time to evolve without cross-modal leakage during the early period (3.5 to 0.6Myr) and even has a couple of hundred-thousand years to become fully linguistic after hominins start to play with fire (0.8 to 0.6My).
So, synaesthesia would not make a jump from things themselves to vocal utterances, but from manual-brachial word-gestures to vocal utterances.
Suddenly, synaesthesia no longer seems implausible.
0244 Second (B), compare Mithen’s nyet hypothesis with Jaynes’s proposal of the bicameral mind.
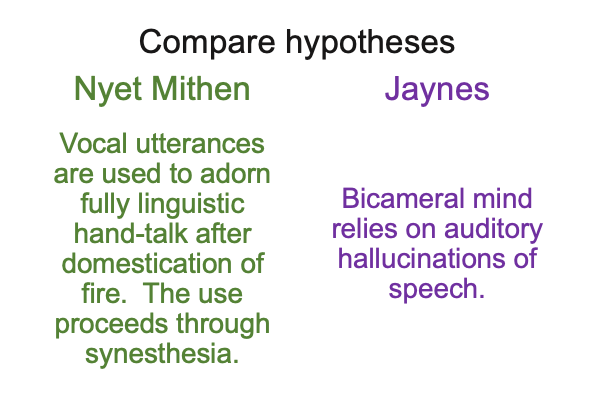
To me, the idea that manual-brachial word-gestures provide stimuli allowing synaesthetic crossover from visual to auditory sensations seems like “auditory hallucinations”.
0245 My goal in this first examination is to develop this impression.