Looking at Melinda A. Zeder’s Article (2025) “Unpacking the Neolithic” (Part 1 of 4)
0001 If I may present my conclusion at the beginning, “I suggest the following motto: First the bauplan, then the twist.”
0002 The full title of the essay under examination is “Unpacking the Neolithic: Assessing the Relevance of the Neolithic Construct in Light of Recent Research”. The article appears in the Journal of World Prehistory (2025) in volume 38:11, pages 1-58 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10963-025-09198-0). The author is affiliated with the Department of Anthropology, National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution in Washington D.C.
0003 The author’s argument follows the Greek tradition of (A) setting out prior propositions, (B) adding further information and assessments and (C) proposing one’s own solution.
Prior propositions (A) are covered in the section titled, “The Origin of the Term ‘Neolithic'”.
Further information (B) includes sections on neolithic emergences in southwest Asia and other regions, including China, Japan, eastern north America, Mesoamerica and the northwest America.
The author’s proposal (C) appears in a section titled, “Repackaging the Neolithic”.
0004 I examine each movement in the sequence A, C then B.
0005 In regards to the historical origin of the term, “neolithic” (A), the word appears in the 1850s in the context of prehistoric lithic technology. A distinction between old “paleolithic” and new “neolithic” tools reflects a fairly recent change in the human condition. The Paleolithic extends very far back into the evolution of the Homo genus. The Neolithic is fairly new and applies only to Homo sapiens. By “new”, I mean, say, starting less that 20,000 years ago.
0006 As it turns out, stone tools and fossilized bones are the most recoverable items from the distant past. So, the idea that our kind evolves will of course rely of this type of data. The implications are significant. If lithic technologies are like matter, then the archaeologist may speculate on forms of prehistorical human (or “hominid” or “hominin”) conditions.
0007 For example, the earliest paleolithic stone tools are labeled “Oldowan”. These tools can be made on the fly. If I strike one rock with another, I can fracture off a shard and expose a sharp edge. Of course, one must choose the right rocks for this trick. Plus, technique is important.
Later stone tools are labeled “Acheulean”. These stone tools are made ahead of time, by the same technique of hammering off shards to reveal an intended form that… somehow… is intrinsic to the original rock.
0008 So, what am I suggesting?
Is the actuality of matter and form intrinsic to rocks, and ancestral hominins learn to tamper with one real element (matter) in order to sculpt the other real element (form)?
0009 I am suggesting more than that.
Aristotle’s hylomorphe (hylo = matter, morphe = form) is an exemplar of Peirce’s category of secondness. Secondness consists of (at least) two contiguous real elements. For paleolithic hominins, a rock (matter) could be sculpted into a stone tool (form). From the point of view of the archaeologist, the hylomorphic structure still applies. The question is, “How?”
Paleolithic stone-tool technology “sculpts” prehistorical human conditions.
0010 Of course, the word, “sculpts”, serves as an aesthetic metaphor for the contiguity between paleolithic technology as matter and hominin conditions as form.

0011 The challenge for nineteenth-century anthropology is clear. Propose a better, more scientific, or at least, less metaphysical, label for the contiguity.
With only geological strata, stone tools and fossilized bones as evidence, proposals were necessarily speculative. But, archaeologists continued digging, and by the 1850s could make the distinction between paleolithic and neolithic. Also, they figured out a reason for why the advance from Oldowan to Acheulean stone tools “sculpted” more advanced hominin conditions. Man was making himself.
0012 What do these evidential and rational developments suggest?
For a Peircean, secondness is the dyadic realm of actuality. Secondness is only one of Peirce’s three categories. The other two are thirdness (the triadic realm of normal contexts, judgments, signs, mediations and so forth) and firstness (the monadic realm of possibility).
Each of these categories manifests its own logic. Also, each higher numbered category prescinds from the adjacent lower category. Thirdness prescinds from secondness. Secondness prescinds from firstness. Prescission allows the articulation of the category-based nested form, as described in Razie Mah’ e-book, A Primer on the Category-Based Nested Form.
0013 Thirdness bring secondness into relation with firstness.
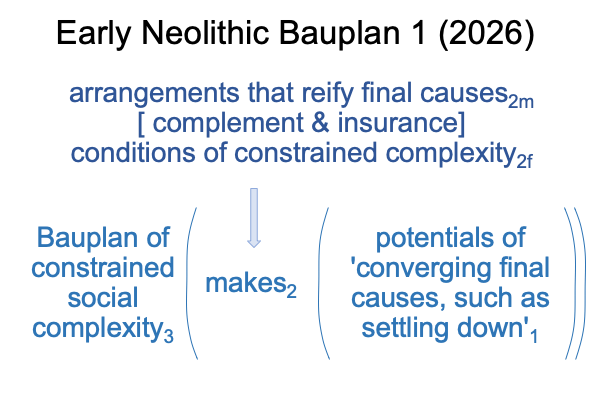
A triadic normal context3 brings a dyadic actuality2 into relation with the possibility of ‘something’1.
0014 Now I can slide the above dyad into the slot for actuality2 for the category-based nested form intimated by the title of V. Gordon Childe’s 1936 book, Man Makes Himself.
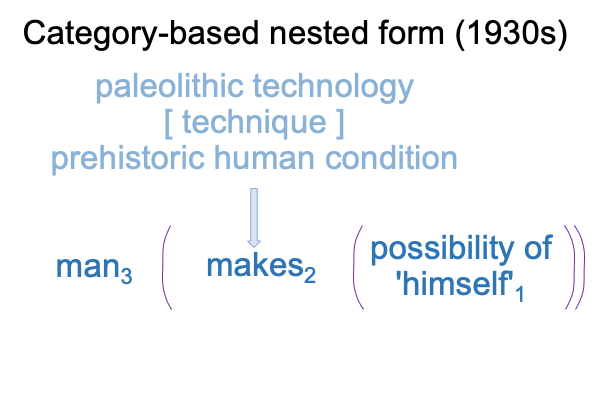
0015 The slide clarifies the contiguity, paleolithic technology constellates a substance, which I label, “technique”, that manifests an essence for the conditions of evolving hominins (that is, a substantiated form).
Consequently, the appearance of a new stone tool technology indicates a change in techniques as well as a change in the essence of the prehistoric human condition.
0016 According to Childe (1892-1957), the “neolithic” label encompassed more than a change in lithic technology. The prehistoric human condition gets entangled with all sorts of other matters, including sedentary communities, economies of delayed returns, various modes of storage and so forth. A long list of material arrangements gets entangled.
0017 As it turns out, once matter substantiates form, then form can entangle other matter, which is a confounding. Here, “confounding” is a technical term, precisely labeling one form originating from one matter and entangling another matter.
Historically, a confounding is an idea that belongs to Aristotle’s tradition. It is stumbled upon long after Aristotle’s campus went out of business. It is the brainchild of the Byzantine and Slavic civilizations.
0018 Here is a picture of Childe’s confounding.
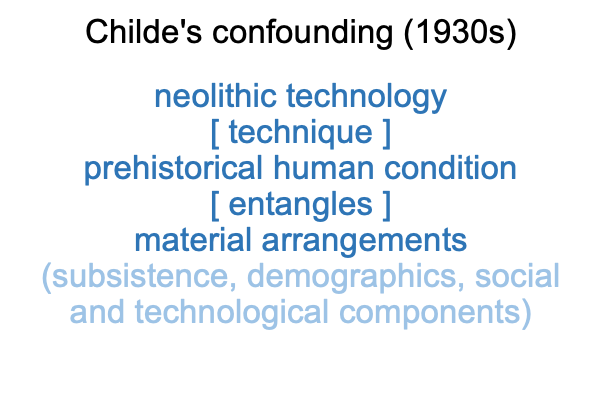
0019 The upper three lines presents the neolithic thing. Neolithic stone-tool technology [substantiates] the prehistoric human condition. The nature of the [substance] is labeled, “technique”.
The lower two lines presents the entangled matter. The [entanglement] is difficult to label, because its nature is.. well… a long list of material arrangements.
0020 A list of material arrangements appears in Table 1 of the article. Even the social components of social mechanism, magico-religious sanctions and trade can be shoved under the rug labeled, “material arrangements”.
0021 As such, the “neolithic” may serve as an adjective to a noun, “revolution”, that appeals to academics sympathetic to Marxist formulations. Yes, they are the ones who only promote academics with similar sympathies. Also, Childe was… um… a sympathizer.
The question is not about whether prehistoric folk are “communist” or “fascist”, even though these labels may apply to this or that anthropologist of the 1930s.
The question is whether the Marxist formula applies to prehistoric folk.
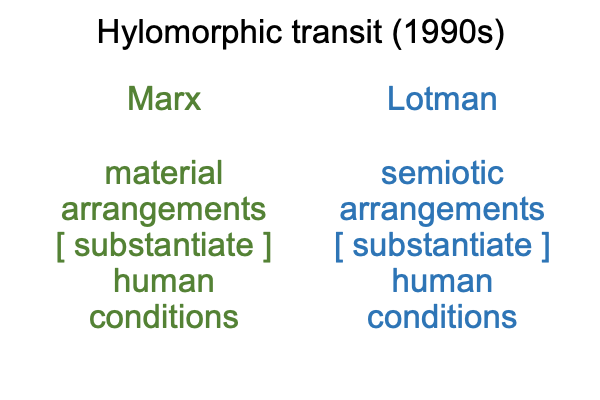
0022 The answer becomes obvious, when Childe’s confounding resolves into the following hylomorphic structure.

0023 The above figure depicts a Marxist version of Aristotle’s hylomorphe, {matter [substantiates] form}. Childe’s hylomorphe lasts for nine decades (that is, until the present day at the start of 2026). Man makes himself through a standard Marxist formulation. Soon, Soviet era archaeologists adopt the stance that the appearance of pottery is a hallmark of neolithic emergence. Pottery is a material arrangement. The emergence of the neolithic is a human condition.