Looking at Alexei Sharov’s Chapter (2024) “Semiotics of Potential Meanings” (Part 1 of 8)
0901 The text before me is chapter seven of Pathways (see point 0831 for book details, pages 137-166).
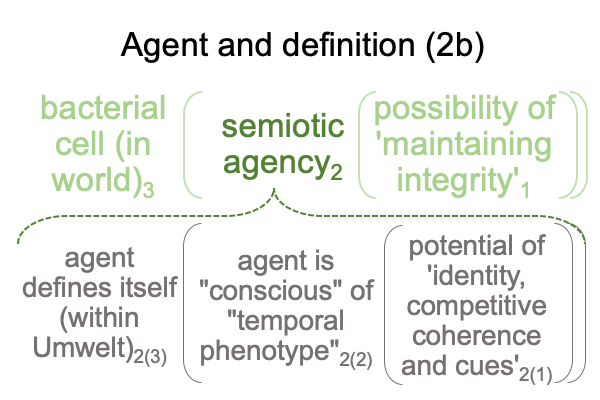
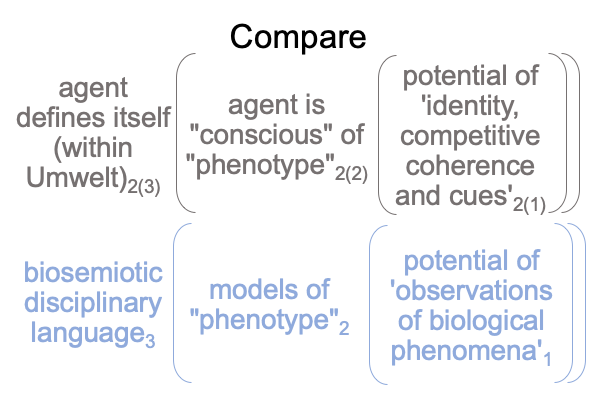
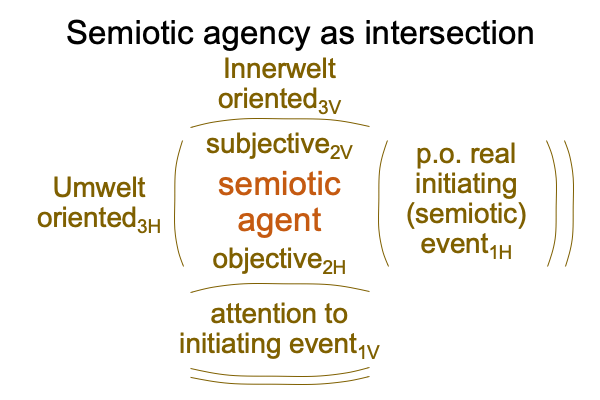
Examinations of the chapters on non-human agency end up with a suggestion that biosemiotics may include more than semiotic agency. Semiotic agency contains the specifying and exemplar sign-relations. The scholastic interscope for how humans think contains one other sign-relation. The interventional sign-relation is odd, compared to the other two sign-relations.
So is the author’s term, “potential meanings”.
0902 Of course, the terms, “interventional sign-relation” and “potential meanings” are mere labels. They are tags. They are spoken words. They are unlike the manual-brachial word-gestures of fully linguistic hand or hand-speech talk.
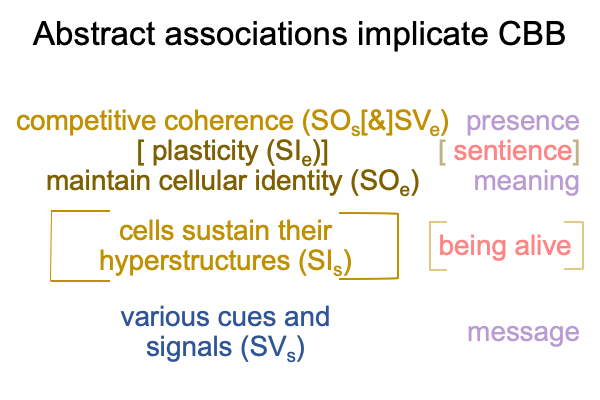
For hand talk, in terms of parole, gesture-words picture and point to their referents. They are icons and indexes. So, word-gestures (SVs) abstract the natural sign-qualities of these types of signs. Icons and indexes picture and point to ‘something that could be present’ (SOs). Presence (SVe) can have many meanings, depending on what is going on. Consequently, SOe is an intuitive abstraction based on what the word-gesture implicitly pictures and points to(langue). I call the process, “implicit abstraction”.
For example, the hand-talk word, [image RAVEN], can denote the color black, as well as particular attitudes.
The hand-talk word, [POINT to corner of eye], can denote the color white, as well as particular attitudes and warnings.
0903 Can the term, “potential meaning” be stated using hand-talk?
No. What is there to picture or point to?
The term is an explicit abstraction.
0904 In speech-alone talk, parole is arbitrarily related to langue.
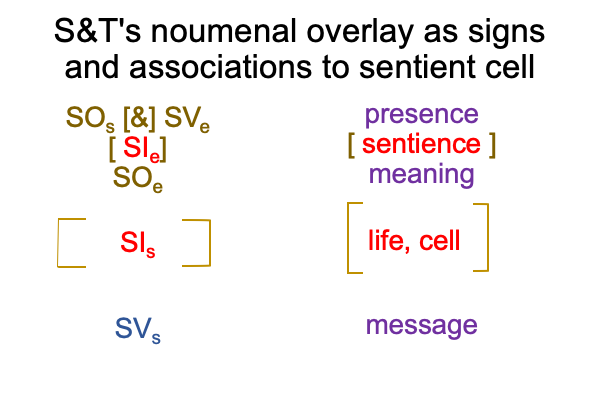
Since parole comes first, as SVs, the specified referent (SOs) comes into being after a word is spoken. After all, SVsassociates to message and message precedes presence (SOs). The specified referent (SOs) associates to information2b. But, since speech-talk cannot picture or point to anything, that information2b (SOs) may end up being explicitly defined.
0905 I say “may”, because sometimes information2b is obvious. Consider the word, “chair”. Everyone immediately intuits a “chair”, even though chairs do not occur in nature. But, what about the American bureaucratic designation, “chair-person”?
Sit down for a minute and think about it.
How can a person be a chair?
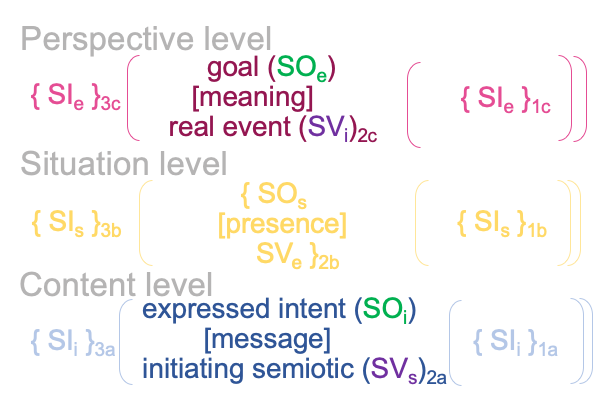
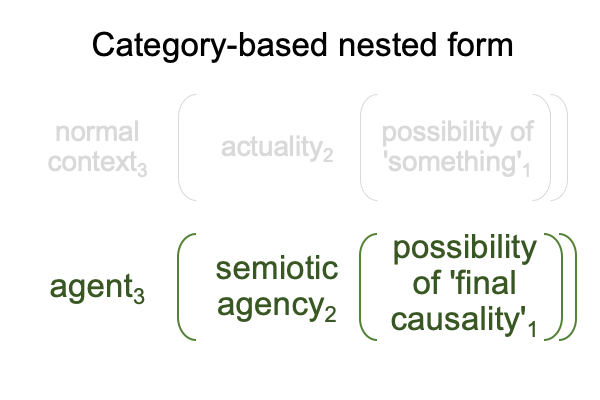
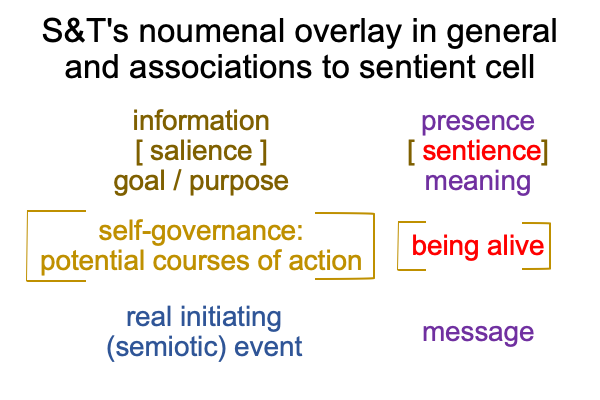
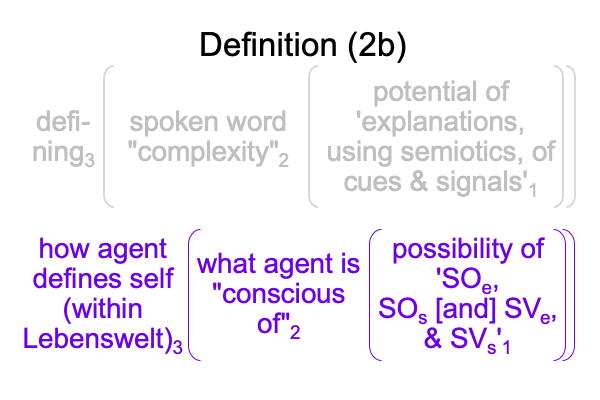
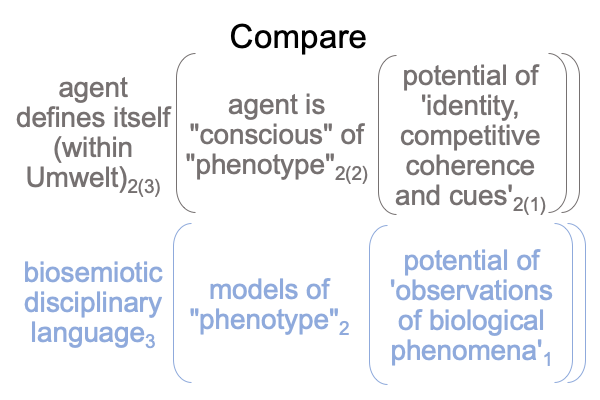
0906 Sharov’s technical term, “potential meaning” has two descriptors made into one character. So, one way to approach the term is to step back and consider the initial claim made in Razie Mah’s e-book, How To Define The Word “Religion” (available at smashwords and other e-book venues). The normal context of definition3 brings the actuality of a spoken term2 into relation with the potential of its meaning, presence and message’1.
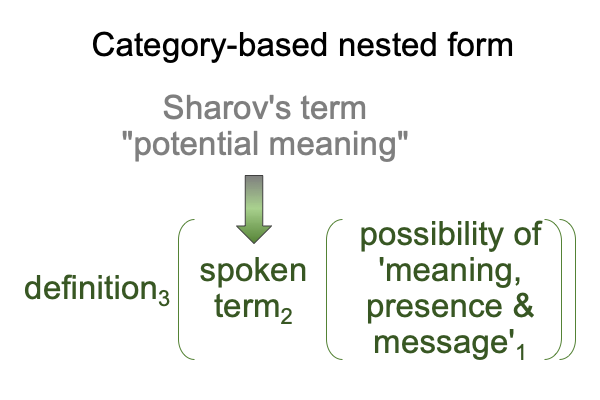
0907 Surely, the reader anticipates my next move.
The words that go into the slot for potential1 are familiar.
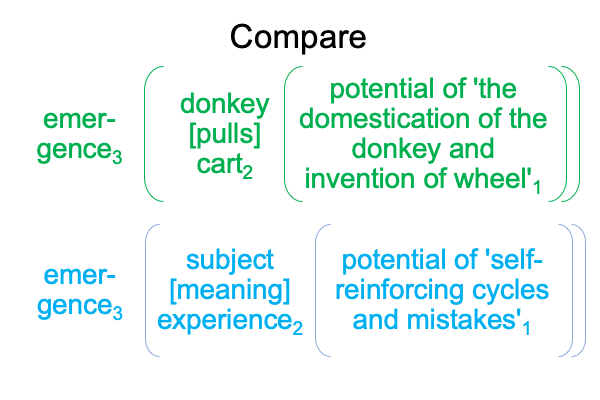
Not only do they1 underlie the actuality of a spoken term2, they1 have already been used to label the three intra-level contiguities that occur in the biosemiotic noumenal overlay.
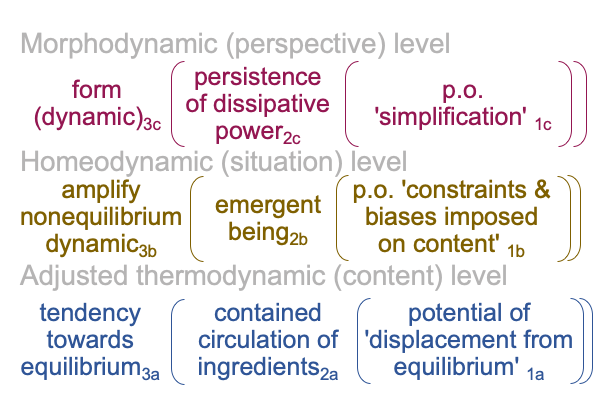
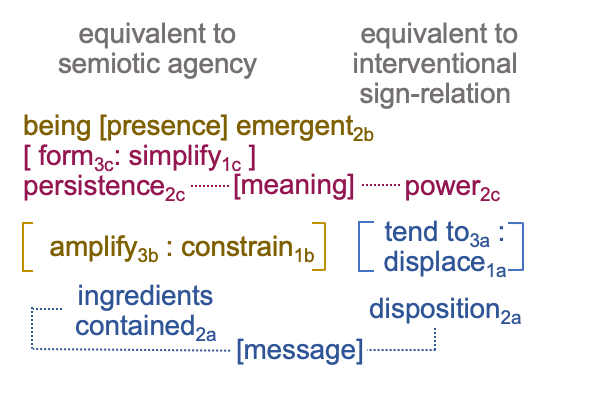
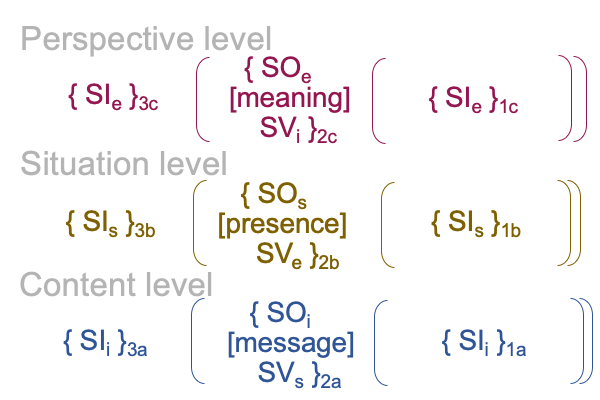
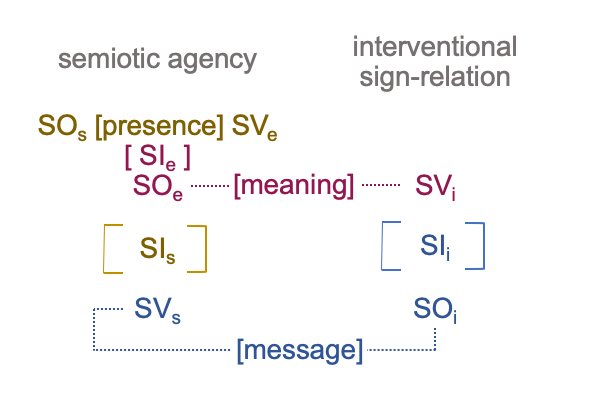
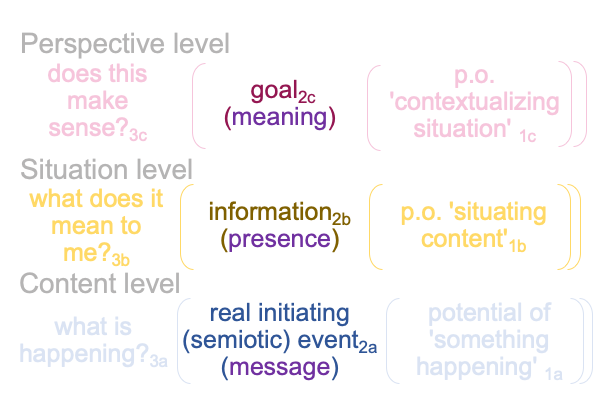
0908 Here is a picture.
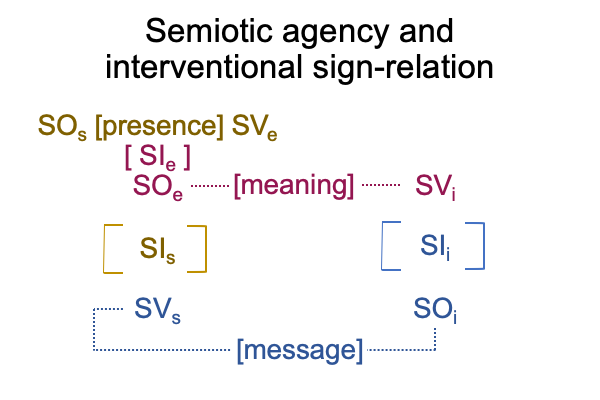
Since [meaning] is the one contiguity that associates to “meaning”, [presence] and [message] must associate to the qualifier, “potential”