0006 Unlike the cat, the dog has a tool of the intellect, whose application is so relevant that it fashions the ways that the species adapts into its niche. This raises the question, “What is a niche?”
0007 First, an aside. The interscope for the Darwinian paradigm is developed in Comments on Dennis Venema and Scot McKnight’s Book (2017) Adam and the Genome and is represented in other e-books and blogs by Razie Mah. The two-level interscope is presented in A Primer on Sensible and Social Construction, available at smashwords and other e-book venues.
0008 Second, an answer to the question.
A niche is the (situation-level) potential1b of a (content-level) actuality that is independent of the adapting species2a. As such, the niche1b underlies the actuality of adaptation2b in the normal context of natural selection3b. Here is a picture.
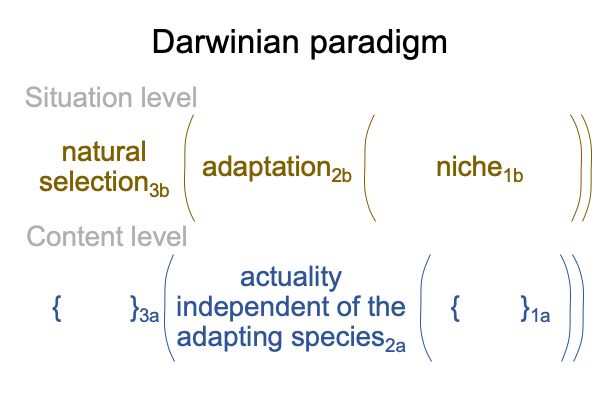
0009 On the situation level, the normal context of natural selection3b brings the actuality of an adaptation2b into relation with its niche1b, which is the potential1b of an actuality independent of the adapting species2a.
As mentioned earlier, the dog has a tool of the intellect and this tool must be an adaptation2b. What is the dog’s niche1b? It must be us, humans, of course. We are the actuality independent of the adapting species2a. When we look at the dog’s adaptations2b from our point of view, we call the result, “domestication”. The dog finds a pack in the human household.
0010 Of course, the dog’s domestication is a recent process.
How did it happen?
Certain wolves, empowered by humans, learn to identify the human as a candidate for a pack leader. Surely, humans are more… um… humane, depending on how one defines the word, “humane”. When a dog is treated like a member of the family, more or less, its descent from wolves serves it well, since a wolf knows that it belongs to a pack. A lone wolf is unlikely to survive on its own. Dogs know this and therefore, accept the leash.
0011 I wonder whether Dennett would call the dog’s affection for its new-found pack leader “an evolved user illusion”. Whatever label one wants to apply, the dog’s affection serves as a conviction, or rather, a judgment. A judgment is a triadic relation with three elements: relation, what is and what ought to be. A relation (in the dog’s being) brings what is(a human, especially when it provides food and family) into relation to what ought to be (a pack leader for the domesticate).
The dog signifies its joy, as well as its distress, through its tail.
What a tale the dog’s tail tells!
0012 No matter what the content-level normal context3a or potential1a, the dog’s tail specifies its consciousness of whether its gambit2b is working.
But, with that said, I seem to have entered a different paradigm. This paradigm belongs to old-fashioned Latin schoolmen, called “scholastics”, who prospered between say, 800 to 1700 AD, from the very end of the Roman empire to the start of the modern era.
0013 If I say that the canine’s tail tells me something about what is going on in the dog’s mind, irrespective of what is happening3a and the potential of ‘something’ happening’1a, then I may conclude whether the dog is happy or not2b, by situating a dog’s tail action1b in the normal context of what it means to me3b.
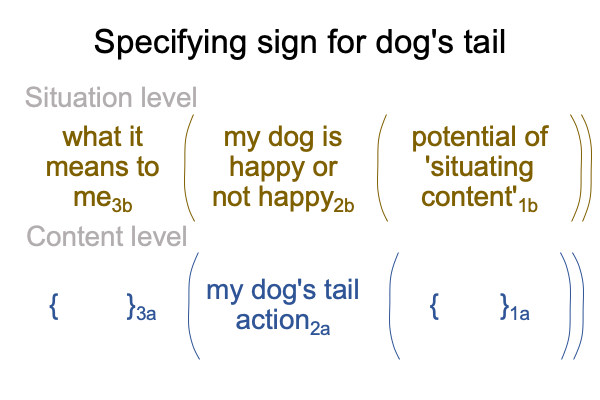
The specifying sign is a triadic relation where a sign-vehicle (SV) stands for a sign-object (SO) in regards to a sign-interpretant (SI).
My dog’s tail action2a (SVs) is the sign-vehicle for a specificative sign-relation.
The happiness or unhappiness of my dog2b is the sign-object (SOs).
What it means to me3b and the potential of ‘situating content1b is the specifying sign’s interpretant (SIs).
If my dog wags its tail (SVs), then I know that my dog is happy (SOs).
If my dog tucks its tail between its back legs (SVs), then I know that my dog is not happy (SOs).
0014 I wonder whether one dog notices the tail-action of other dogs. After all, for all dogs, only content and situation levels matter. So, I suppose that they do. The tail-wagging and tail-tucking business may have been enhanced because humans are receptive to such signals.
0015 Would Dennett call a dog’s tail action a “meme”?
I suspect that he would.
0016 Meanwhile, premodern scholastics call the above two-level interscope, “specificative extrinsic formal causality”. I call it “a specifying sign”.
Tail-action2a is the sign-vehicle (SVs). My dog’s apparent attitude2b is the sign-object (SOs). The normal context of what it means to me3b, operating on the potential of ‘situating content’1b is the sign-interpretant (SIs). The subscript stands for “specifying”.
The sign-relation is discussed in detail in Razie Mah’s blog for November 2023, Looking at John Deely’s Book (2010) Semiotic Animal, as well as A Primer on Natural Signs and related e-articles available for sale at smashwords and other e-book venues.
