0030 In chapter nine, on evolution and human ethics, Domning envisions a short step from an amoral psychology (original selfishness) to a moral psychology associated with Original Sin (human selfishness). All that is required is the evolution of creatures capable of self-reflection.
Is that the same as the evolution of self?
Or, is that the evolution of cupid, the self in the presence of others?
Uh oh, the term, “cupid”, now has a technical definition.
0031 Is our capacity for self-reflection an adaptation into an ultimate niche or is it an evolutionary spandrel, an architectural feature of adaptations into diverse proximate niches?
Domning suggests the latter, by noting that intelligence is a composite of a wide variety of faculties, many of which are contradictory. Trade-offs favor a psychological ambivalence, which looks more and more like free will.
Does this imply that human free will arises from a diversity of “original selfishnesses”, each specific to a dilemma in the environment of evolutionary adaptation, psychologically expressed as behaviors consistent with the emphatic, I-myself?
So, the “self” seems to be a spandrel, where all these architectural (and archetypal) psychologies come together to form something, that ends up labeled as “self”.
0032 Remember this one?
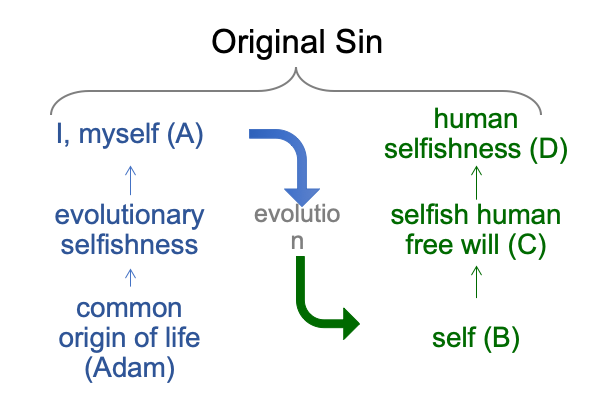
0033 Item A entails no moral deliberation.
Item D involves moral deliberation.
0034 Item B, the consolidation of psychological expressions of I-myself into a single entity, the self, does not entail moral deliberation.
Item C, the tendency to put one’s own interests above other interests in the exercise of human free will, implicates moral deliberation.
0035 Now, I would like to substitute my newly minted technical term, “cupid” (B’), in for “self” (B) and see what happens.
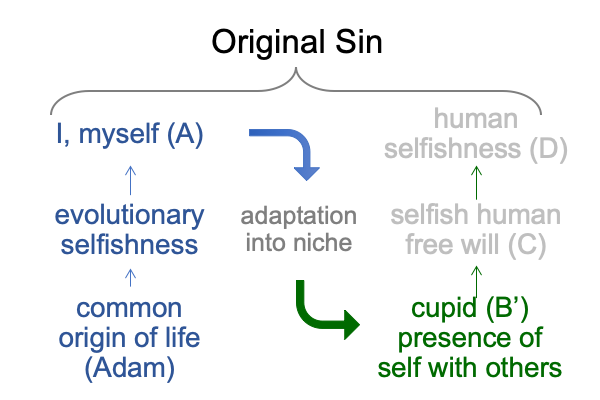
0036 Right off, the nature of “cupid” as an adaptation accounts for the spandrel-like “self”. Its niche entails some sort of judgment (a triadic relation) in which the self is socially constructed out of a variety of psychological expressions of I-myself.
Here is the key.
Psychologically, self-interest is composed in response to other selves. Cupid is the self becoming aware of its own self-interests in a social world where others exhibit their own interests through psychological expressions of I-myself. In order to consolidate my self, from my own expressions of I-myself, I must consolidate the selves of others, from their own expressions of I-myself.
In brief, the self (B) does not arise in a vacuum. Cupid (B’) designates that fact.
